How to Say No to Cyber Defamation?
In recent years, a number of online defamation cases have aroused widespread concern in society, including the "defamation case of a woman taking delivery of a courier", which has been named by the Supreme People's Procuratorate and has become a typical case. The victim of the case, Gu Moumou, was secretly filming a video by a stranger, Lang Moumou. Later, Lang Moumou and He Moumou jointly slandered Gu Moumou as a "derailed courier". The two people faked the identities of Gu Moumou and the courier and fabricated chat records, and forwarded the fabricated chat records and the secretly captured video to WeChat group. Later, these contents were spread to many WeChat groups and WeChat official account, causing a large number of clicks, reading and vulgar comments, causing hot online discussions. The victim, Gu Moumou, suffered a lot of abuse and bad reviews as a result, became depressed and was tactfully persuaded to quit by the company. Gu Moumou couldn't bear the humiliation and reported the case to the public security organ, which took administrative detention measures against the online defamation perpetrators Lang Moumou and He Moumou. However, even after being detained administratively, Lang and He refused to repent and apologize to the victim Gu. In order to argue for a statement, Gu Moumou filed a criminal private prosecution with the Yuhang District People's Court of Hangzhou City, requesting that the two persons be held criminally responsible for their actions, which constituted a crime of libel. After the court accepted the criminal private prosecution filed by Gu, the Yuhang District People's Procuratorate of Hangzhou City recommended that the Yuhang Branch of the Hangzhou Public Security Bureau file a case for investigation of Lang and He suspected of defamation. Subsequently, the Yuhang District Procuratorate filed a public prosecution with the court on the grounds that the actions of Lang and He were suspected of constituting a crime of defamation. This case was converted from a private prosecution case to a public prosecution case. After the court heard the case, it was finally judged that the actions of Lang and He constituted a crime of defamation. The two persons were sentenced to one year's imprisonment and two years' probation. The victim Gu finally waited for justice.
However, in online defamation cases, the transition from private prosecution cases to public prosecution cases is rare, and a large number of cases are still the norm for victims to initiate criminal private prosecution or initiate civil litigation for infringement of reputation disputes to safeguard their rights and interests. Most cases have not become public prosecution cases. According to the statistical data from the "Search Report on Similar Cases of Online Defamation" of the School of Law of Hunan Normal University, there were 133 defamation cases occurred in the online environment from January 1, 2018 to June 30, 2020, with public prosecution cases accounting for 21.05% and private prosecution cases accounting for 78.95%. Due to the anonymity and complexity of the network environment, victims of online defamation cases generally face the dilemma of obtaining evidence, and it is difficult for victims to effectively safeguard their legitimate rights and interests by relying on their own efforts. When encountering online defamation, how can the victim take up the weapon of the law to say no to online defamation? This article aims to provide some practical suggestions for victims of online defamation.
1、 What are the legal consequences of online defamation?
Cyber defamation may involve three types of legal liabilities: civil, administrative, and criminal. The severity of the three types of legal liabilities is gradually increasing. Bearing civil liability may not limit personal freedom, but bearing administrative responsibility may restrict personal freedom or be fined. However, bearing criminal responsibility constitutes a crime, and may result in criminal coercive measures and penalties. Different legal responsibilities involve different legal bases, identification standards, and ways of assuming responsibility. When the same online defamation act simultaneously meets the standards for determining civil, administrative, and criminal liability, the victim can either claim that the online defamation perpetrator bears any one of these legal liabilities, or claim that the online defamation perpetrator bears two or three types of legal liabilities.
(1) Civil Liability for Network Defamation
Civil liability refers to the adverse civil legal consequences that should be borne due to civil violations, breach of contract, or legal provisions.
1. Legal basis
Article 1024, 179, 1182, and 1183 of the Civil Code of the People's Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as the "Civil Code"); "Provisions of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law to the Trial of Civil Disputes over the Use of Information Networks to Infringe Personal Rights and Interests", Articles 11 and 12
2. Recognition criteria
In the field of civil law, online defamation belongs to civil tort, which infringes on the reputation rights of victims. Meeting the following constitutive requirements constitutes cyber defamation:
(1) Infringement of the reputation rights of victims by online defamation perpetrators by fabricating facts and disseminating them on information networks; (2) The perpetrator of online defamation is at fault (intentional or negligent); (3) If the victim's reputation right is infringed, there will be infringement results; (4) There is a causal relationship between the infringement behavior of the online defamer and the infringement result.
3. Legal Consequences
According to the law, victims can claim the following civil liabilities from online defamers:
(1) Stopping infringement requires the online defamer to stop the ongoing infringement and delete the content of the defamation victim posted by the online defamer on the network.
(2) To compensate for losses, the victim may request the online defamation perpetrator to compensate for property losses and spiritual losses, pay reasonable expenses for the victim or entrusted agent to investigate and obtain evidence of the infringement, as well as legal fees that comply with the regulations of relevant national departments.
(3) Eliminate impact and restore reputation
Victims can request the perpetrators of online defamation to publicly acknowledge the infringement, clarify the facts, and eliminate the adverse effects within the scope of the impact of online defamation, in order to restore the social evaluation of victims when their reputation rights are not damaged.
(4) Apologize
The victim may request the online defamation perpetrator to publicly apologize to the victim within the scope of the impact of online defamation.
(2) Administrative Responsibility for Network Defamation
Administrative responsibility refers to the sanctions imposed by national administrative organs or authorized units on units and individuals who violate laws and regulations in accordance with administrative procedures, including administrative penalties and sanctions.
1. Legal basis
Article 42 of the Law of the People's Republic of China on Administrative Penalties for Public Security; "Guidelines for the Determination of Punishment by Public Security Organs for Some Violations of Public Security Management" Part II: Determination Criteria for Specific Acts Article 36
2. Recognition criteria
Conforming to the following constitutive requirements, online defamation perpetrators need to bear administrative responsibility: (1) fabricating facts to slander others; (2) There is an intentional libel.
Under any of the following circumstances, it shall be considered as "the circumstances are relatively serious" in Article 42 of the Law of the People's Republic of China on Administrative Penalties for Public Security:
(1) Using bad means or methods; (2) Causing a significant impact on the normal work, life, physical and mental health, or reputation of others; (3) Failing to stop after being dissuaded; (4) Using information networks to slander others; (5) Implemented for multiple people; (6) Other serious circumstances.
3. Legal Consequences
Be detained for not more than five days or fined not more than 500 yuan; "If the circumstances are relatively serious, they shall be detained for not less than five days but not more than 10 days, and may also be fined not more than 500 yuan.".
(3) Criminal Liability for Cyber Defamation
Criminal responsibility refers to the consequences of sanctions imposed by the court in accordance with criminal law on the perpetrator for committing a criminal act. It is the most severe form of legal responsibility, and criminal responsibility is mainly achieved through punishment.
1. Legal basis
Article 246 of the Criminal Law of the People's Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as the Criminal Law); Article 1, Article 2, and Article 3 of the Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in Handling Criminal Cases such as Using Information Networks to Implement Defamation
2. Recognition criteria
Whether online defamation constitutes a crime of defamation depends on whether the act of online defamation meets the criminal constitutive requirements of the crime of defamation. The constitutive elements of the crime of defamation include the main elements, subjective elements, object elements, and objective elements.
(1) Subject Elements
Including: a. those who fabricate defamatory information and disseminate it on the information network; B. Those who tamper with original information as defamatory information and disseminate it on the information network; C. Those who knowingly disseminate false defamatory information on the information network.
(2) Subjective Elements
For those who fabricate defamatory information and disseminate it, and those who tamper with the original information as defamatory information and disseminate it, both are required to have the intention of defamation; For the disseminator, it is required to know clearly that the information forwarded is fabricated and harmful to the reputation of others.
(3) Object Elements
Cyber defamation infringes upon the victim's right to reputation.
(4) Objective elements
The objective elements include three aspects: the mode of conduct, the object of conduct, and the seriousness of the circumstances.
Behavioral methods include: a. fabricating facts that harm the reputation of others, spreading them on the information network, or organizing or directing personnel to spread them on the information network; B. Tampering the original information content involving others on the information network into a fact that damages the reputation of others, spreading it on the information network, or organizing or directing personnel to spread it on the information network; C. knowingly fabricating facts that harm the reputation of others and spreading them on the information network, resulting in a flagrant situation.
The object of behavior is a specific natural person.
Serious circumstances refer to the following situations: a. The same defamatory information has actually been clicked or viewed more than 5000 times, or has been forwarded more than 500 times; B. Causing serious consequences such as mental disorder, self mutilation, suicide, etc. of the victim or his close relatives; C. Within two years, he has been subjected to administrative penalties for defamation and slandered others; D. Other serious circumstances.
3. Legal Consequences
Shall be sentenced to fixed-term imprisonment of not more than three years, criminal detention, public surveillance, or deprivation of political rights.
2、 How should victims protect their rights?
Step 1: Collect and preserve evidence according to law
1. Evidence content to be preserved
The victim cannot only save online links, but also needs to save screenshots of online defamation content, such as WeChat chat records, Weibo, clients, news, posts, emails, and other web pages or APP page screenshots. If there are videos, they should also be downloaded and saved.
2. Means and methods of preserving evidence
"Because the content of online defamation may be deleted at any time by the online defamer, resulting in the loss of evidence, in order to avoid the adverse consequences of the victim's inability to provide evidence, the victim should adopt appropriate means and methods to preserve evidence.". In addition, in order to better ensure the integrity and legitimacy of the evidence, lawyers suggest that victims use data rights protection platforms (such as the Joint Trust Timestamp Service Center, the IP360 Open Platform for All-round Data Rights Protection, etc.) or go to a notary office to secure evidence. Because data rights protection platforms typically use tamper resistant technical means to secure evidence, and can be authenticated through electronic forensics and evidence storage platforms, while parties involved in notarized documents do not need to provide evidence to prove the facts.
Step 2: Inform the network service provider and require the network service provider to take necessary measures such as deleting, blocking, and disconnecting links for content suspected of network defamation. At the same time, require the network service provider to disclose information such as the name, contact information, and network address of the suspected infringing network user.
"While sending a notification to the network service provider, the victim should provide the network service provider with their true identity information and preliminary evidence of infringement by the network user.". The victim may also entrust a lawyer to send a lawyer's letter to the network service provider requesting the network service provider to take necessary measures and disclose the identity information of the suspected infringement network user.
Step 3: According to different infringement situations, victims can choose to take one or all of the following rights protection methods to investigate the different legal responsibilities of online defamation perpetrators:
(1) How to investigate the administrative responsibility of the perpetrators of online defamation?
According to Article 11 of the Regulations on the Procedures for Handling Administrative Cases by Public Security Organs, victims can report to the following public security organs with jurisdiction:
(1) The network used by the perpetrators and victims of online defamation and the location of their operators; (2) The location where the victim was injured; (3) The place where the victim's property has been damaged.
In order to facilitate the reporting of the victim, the lawyer recommends that the victim report the case to the police station at the location of the network he uses or the location where he was injured.
After accepting the case, the public security organ will conduct an investigation in accordance with the law and make a punishment according to the evidence obtained from the investigation. If the investigation determines that the defamation facts of the perpetrator are established, the perpetrator of online defamation will be detained for not more than five days or fined not more than 500 yuan. If the defamation is serious, the perpetrator of online defamation will be detained for not less than five days but not more than 10 days, and may also be fined not more than 500 yuan.
(2) How to investigate the civil liability of the perpetrators of online defamation?
Victims can pursue the civil liability of the perpetrators of online defamation by filing a civil lawsuit in a people's court.
Who will take responsibility?
(1) Network defamation is a situation where network users use network services to implement it
After the victim sends a notice to the network service provider to take necessary measures to delete and block the disconnection of links, and the network service provider promptly takes the necessary measures mentioned above, the network service provider does not need to bear civil liability to the victim, but only the network user bears legal liability.
If the network service provider fails to take necessary measures in a timely manner after receiving the victim's notification, it shall bear joint and several liability with the network user for the expanded portion of the damage.
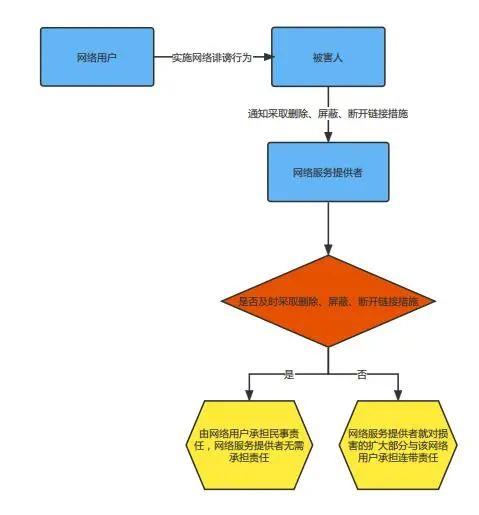
B. If the network service provider knows or should know that a network user has infringed upon the civil rights and interests of others by using its network services, and fails to take necessary measures, it shall bear joint and several liability with the network user.
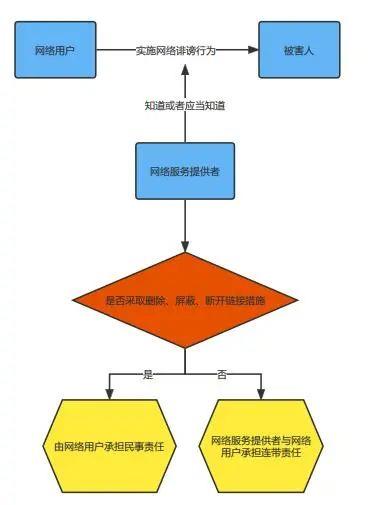
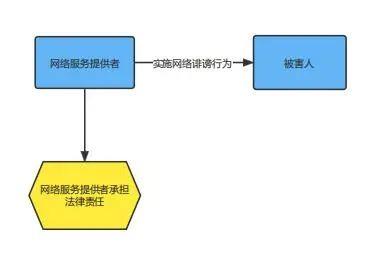
(2) Network defamation is a situation where the network service provider undertakes the tort liability.
Who will be chosen as the defendant?
As mentioned earlier, the subject of civil liability for online defamation needs to be determined in combination with specific circumstances. For victims:
(1) If online defamation is committed by an internet user and the victim knows the identity information of the internet user, the victim can either list only the internet user as the defendant or list the internet service provider and the internet user as co defendants. If the victim does not know the identity information of the network user, he or she may only list the network service provider as the defendant, and request the court to order the network service provider to provide the people's court with information such as the name, contact information, and network address of the network user who can determine the infringement. After obtaining the aforementioned information, the network user may be added as the defendant.
(2) If network defamation is committed by a network service provider, the network service provider is listed as the defendant.
(3) If network defamation is implemented jointly by network service providers and network users, the network service providers and network users are listed as joint defendants.
In which court did you sue?
The victim may bring a lawsuit to a court with jurisdiction in the place where the victim has his domicile, the place where the online defamation perpetrator has his domicile, or the place where the information equipment such as the computer of the alleged infringement is located. For victims, lawyers suggest that it is more convenient for victims to choose a court with jurisdiction in their place of residence.
What litigation claims can be filed?
When prosecuting, the victim can submit a lawsuit request to the suspected infringement network user or network service provider to stop the infringement, apologize, eliminate the impact, restore reputation, and compensate for losses.
In addition, in the event that the identity of the suspected infringing network user cannot be determined and the network service provider has to be sued, the victim can claim disclosure of the identity information of the suspected infringing network user and the number of clicks, browses, and forwards of defamatory information from the network service provider. Regarding the manner and scope of apology, victims can claim that the online defamer publicly apologizes on the online platform where he or she committed the defamation.
What evidence needs to be prepared?
(1) The defendant in the prosecution is evidence of the perpetrator of online defamation (such as evidence of the identity information of the network user disclosed by the network service provider to the victim, self admission of the network user, identity information of the network user, etc.);
(2) Using a data rights protection platform or through notarization to provide fixed evidence of online defamation behavior and circumstances;
(3) If the victim suffers from depression due to online slander, a hospital diagnosis certificate and medical fee payment certificate can be provided;
(4) Reasonable expenses for victims to investigate and obtain evidence of infringement (such as notarial fees invoices, payment vouchers)
(5) The agency contract, lawyer's fee invoice, payment voucher, etc. of the entrusted lawyer. According to Article 12 of the "Provisions of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in the Trial of Civil Disputes over the Use of Information Networks to Infringe Personal Rights and Interests", the people's court may, based on the request of the parties and the specific circumstances of the case, calculate the lawyer's fees that comply with the provisions of relevant national departments within the scope of compensation.
(3) How to investigate the criminal responsibility of the perpetrators of online defamation?
According to the provisions of the Criminal Law of China, the crime of defamation generally belongs to a case of private prosecution. Only when the act of defamation reaches a level that seriously endangers social order and national interests, can the criminal case be filed by the public security organ and prosecuted by the procuratorate.
The difference between a public prosecution case for defamation and a private prosecution case is:
(1) The subjects of prosecution are different. Public prosecution cases are initiated by the national public prosecution organ, namely the People's Procuratorate, while private prosecution cases are directly initiated by the victim to the People's Court; (2) The main body of evidence collection is different. In public prosecution cases, the public security organ collects evidence, while in private prosecution cases, the victim usually collects evidence on his own. In cases where there are special provisions in the law, the court can request the public security organ to provide assistance; (3) The degree of harm to crime varies, with criminal acts in public prosecution cases having greater harm to society, while criminal acts in private prosecution cases having less harm to society; (4) The litigants have different litigation positions, and in public prosecution cases, the public prosecution organ is equivalent to the plaintiff's position; The victim in a private prosecution case is a private prosecutor and occupies the position of plaintiff.
As for the crime of defamation, the prosecution must comply with the situation where the defamation act "seriously endangers social order and national interests", specifically including:
A. Causing mass incidents; B. Causing public disorder; C. Causing ethnic and religious conflicts; D. Defamating multiple people and causing adverse social impact; Damage to the national image and serious harm to national interests; F. Causing adverse international impact; Other situations that seriously endanger social order and national interests.
1. Defendants in private prosecution cases
The following subjects can serve as defendants in criminal private prosecution cases of online defamation crimes:
(1) Those who fabricate defamatory information and disseminate it on the information network; (2) Those who tamper with original information as defamatory information and disseminate it on the information network; (3) Those who knowingly disseminate false defamatory information on the information network.
2. Jurisdictional court for private prosecution
According to Article 25 of the Criminal Law, criminal cases are under the jurisdiction of the people's court in the place where the crime was committed. If it is more appropriate to have the case tried by the people's court in the place where the online defamation perpetrator resides, it may be under the jurisdiction of the people's court in the place where the online defamation perpetrator resides. The term "place of crime" herein includes the place where the crime occurred and the place where the result occurred. The place where the criminal act occurred refers to the location of the server and computer information system where the network crime was committed. For victims, it is difficult to determine the place where the criminal act occurred. The place where the result occurs can be understood to include the place where the victim was injured. Therefore, the victim can choose to bring a private prosecution in the court where he or she was located at the time of being infringed or where the online defamation perpetrator resides.
3. Claim for private prosecution
The litigation request generally refers to requesting the court to investigate the criminal responsibility of the online defamation perpetrator (that is, requesting the court to sentence the defamed online user to fixed-term imprisonment of not more than three years, criminal detention, public surveillance, or deprivation of political rights), and may also file a request for criminal incidental civil compensation.
4. Evidence to be provided
The victim also needs to submit evidence to the court when initiating a criminal private prosecution case. The victim can refer to the evidence preparation required for initiating a civil lawsuit case. However, since criminal cases require more strict forms of evidence and standards of proof than civil cases, it is recommended that the victim entrust a lawyer to assist the victim in collecting relevant evidence.
Due to the difficulty in obtaining evidence for online defamation, relying on the victim's own forensic ability, it is difficult to identify the true identity of the perpetrator of online defamation on the one hand, and on the other hand, it is difficult to identify the source of defamation information, as well as the number of clicks, browses, and forwards of defamation information. According to the third paragraph of Article 246 of the Criminal Law, it is indeed difficult for the victim to provide evidence for defamation committed through information networks after initiating a criminal private prosecution, "The people's court may request assistance from the public security organ, so the victim may apply to the people's court to request assistance from the public security organ to provide evidence.".
5. Preparations for criminal private prosecution cases
If the circumstances of online defamation suffered by the victim are serious, the victim can first investigate the civil and administrative responsibilities of the online defamation perpetrator, and in this process, fully collect evidence and obtain the identity information of the online defamation perpetrator and the number of clicks, browses, and forwards of the defamation information, before initiating a criminal private prosecution. If the evidence collected by the victim can prove that the defamation behavior of the online defamer seriously endangers social order and national interests, the victim can try to apply to the public security organ to initiate criminal investigation, and request the public security organ and procuratorial organ to initiate public prosecution procedures for the defamation behavior of the online defamer to investigate their criminal responsibility.
3、 Conclusion
As people often say, the Internet is illegal. Creating a clear and clear network environment requires each of us to consciously abide by laws and regulations and maintain network order. When unfortunately faced with online defamation, the victim cannot be a silent lamb, but should bravely take up legal weapons. Please remember, you can absolutely say no to online slander!
References and Notes:
Chen Dongsheng, Wang Chun, Liu Ya, Wu You. Supreme Prosecutor's Intervention in Judicial Litigation: A Sword for Cyber Defamation. Rule of Law Daily, 2022-2-16 (6)
Xiang Zhiyu, Shen Xueping, Ai Junyi, Plateau, Feng Yangyang, Peng Jiaqian, and Wang Yingyue. Search Report on Cases of Online Defamation https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?src=11 × tamp=1647933201&ver=3691&signature=qIuQIZFxc7ZhxFW-EWwCAtf1pmb2P614aweqYR0byoQRdRVgT2aCqPVVkDpmdKLYByD7FKEFSh5pPUcv7CPTsUuvuHgI3Cfn94pp*CqypARLdL*jM49b*NQV2fOCRcbn&new=1
Gao Mingxuan, Zhang Haimei. The Elements of Execution of the Crime of Defamation Constituted by Internet Defamation and Comments on the Interpretation of "Two High" on Using Information Network Defamation https://www.spp.gov.cn/llyj/201507/t20150713_101302.shtml
Related recommendations
- Can I get a tax refund if my bet fails? ——Comment on the case of Wang and Shanghai Taxation Bureau's refusal to refund taxes
- How shareholders can withdraw their shares Series 2: Company merger, division, or transfer of major assets
- From the Xiao incident to see the complex impact of spousal reporting - a double-edged sword in divorce proceedings
- Analysis of Criminal Legal Risks in Low altitude Economy and Preliminary Exploration of the Road to Criminal Compliance in Low altitude Economy




