Discussion on Enterprise Compliance Construction from the Suspected "Pyramid Selling" Event of Zhang Ting Lin Ruiyang Company (3)
On December 29, 2021, following the explosion of a huge tax supplement fine by "Weiya", just over a week later, "Zhang Ting, Lin Ruiyang, and his wife's company were investigated and punished for pyramid selling" hit the hot spot, with a reading volume exceeding 780 million within 24 hours. This incident involves many legal issues. How do consumers protect their rights? What legal responsibilities will participants at all levels of the "pyramid selling" act bear, and how should they protect their legitimate rights and interests? Why can we continue to operate due to repeated complaints about product quality issues? Should we assume responsibility for product quality and how? Why is the market supervision and administration bureau responsible for the investigation rather than the public security organ? Are pyramid schemes suspected of committing crimes and what crimes may be involved? Many of the above legal issues involve various fields of civil, administrative, and criminal law, and require in-depth research and resolution by professionals.
We now take this event as an opportunity to briefly introduce how laws and regulations identify pyramid selling and its manifestations, and call on enterprises to comply with the bottom line of compliance in their operations.
1、 Basic framework of the "Guidelines for Compliance Management of Central Enterprises (for Trial Implementation)"
This article will understand the basic content of enterprise compliance management by interpreting the "Guidelines for Compliance Management of Central Enterprises (Trial Implementation)" (hereinafter referred to as the "Guidelines") issued by the SASAC of the State Council in 2018.
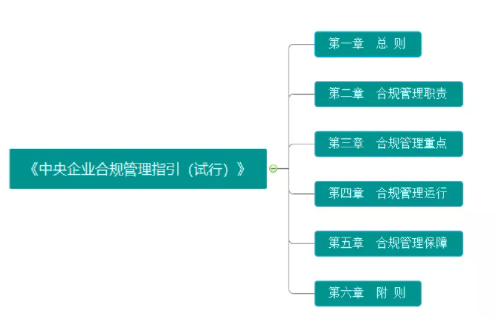
The Guidelines consist of 6 chapters and 31 articles, with the focus on chapters 2-5, which address the issues of who will do it (Chapter 2 Compliance Management Responsibilities), what to do (Chapter 3 Compliance Management Focus), how to do it (Chapter 4 Compliance Management Operations), and how to ensure it (Chapter 5 Compliance Management Assurance). With clear logic and consistent content, it provides a good guidance outline for central enterprises and even the entire Chinese enterprise.
2、 The concept of compliance, compliance risk, and compliance management
"The Guidelines define compliance, compliance risk, and compliance management. Article 2, paragraph 1, stipulates that the central enterprise referred to in the Guidelines refers to a state-owned enterprise that performs the responsibilities of a contributor by the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council.".
The term "compliance" as used in these Guidelines refers to the compliance of central enterprises and their employees' business management behaviors with laws and regulations, regulatory provisions, industry standards, corporate bylaws, rules and regulations, as well as international treaties and rules. Therefore, the scope of "compliance" in enterprise compliance is broader than the scope of "law", which is generally summarized as "external regulations" and "internal regulations". External regulations refer to "regulations" formulated externally by an enterprise, such as laws, regulations, regulatory provisions, etc. Internal regulations refer to the articles of association, rules, and regulations formulated internally by the enterprise, which also includes the internal rules and regulations of the enterprise into the scope of "compliance". In addition, with the development of recent years, enterprise compliance is no longer limited to the above scope, It has been gradually expanded to include business ethics, business ethics, transaction rules, and internal regulations of partners.
The term "compliance risk" as used in these Guidelines refers to the possibility that central enterprises and their employees may incur legal liability, be subject to relevant penalties, cause economic or reputational losses, and other negative impacts due to non-compliance. The main actors of compliance risk include enterprises and employees. Not only may the enterprise bear the risk of non-compliance, but also the risk that individual employees may have negative impacts due to non-compliance; The source of compliance risk is derived from non compliant behaviors, so it is necessary to determine which behaviors are compliant and which behaviors are violations through systems.
The term "compliance management" as used in these Guidelines refers to organized and planned management activities aimed at effectively preventing and controlling compliance risks, targeting the operation and management behaviors of enterprises and employees, including system development, risk identification, compliance review, risk response, accountability, assessment and evaluation, and compliance training. Compliance management is a kind of enterprise management, which is an organized and planned management activity. Its management object is the operation and management behavior of enterprises and employees, and the behavior of enterprises includes the behavior of the decision-making level of enterprises; Management activities include the formulation of compliance management systems, risk identification, review, response, accountability, assessment and evaluation, training, etc.
3、 Who will be responsible for compliance management?
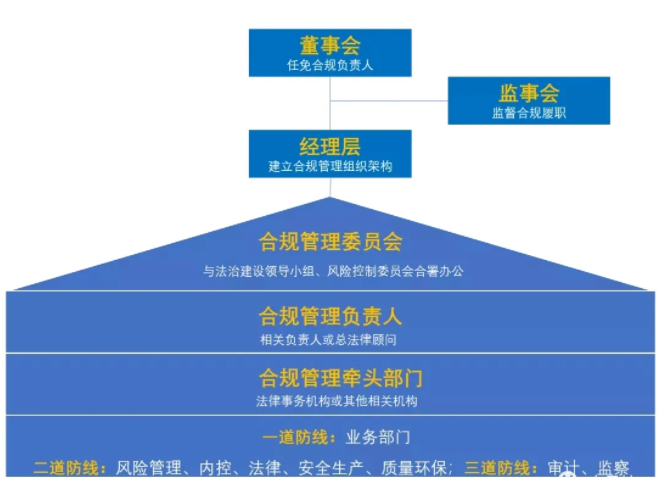
The second chapter of the guidelines stipulates the responsibilities of compliance management, namely, the board of directors decides on the appointment and removal of the person in charge of compliance management and the establishment of the leading department for compliance management; The Board of Supervisors supervises the compliance management performance of the Board of Directors and senior management personnel; Senior management is responsible for compliance management.
1. The responsibilities for compliance management of each organization are:
The compliance management responsibilities of the board of directors mainly include: (1) approving the corporate compliance management strategic plan, basic systems, and annual reports; (2) Promote and improve the compliance management system; (3) Determine the appointment and removal of the person in charge of compliance management; (4) Determine the setting and functions of the compliance management lead department; (5) Study and decide on major issues related to compliance management; (6) Decide on the handling of violators in accordance with their authority.
The compliance management responsibilities of the Board of Supervisors mainly include: (1) supervising the compliance of the decisions and processes of the Board of Directors; (2) Supervise the performance of compliance management responsibilities of directors and senior management personnel; (3) Propose dismissal suggestions for directors and senior managers who are primarily responsible for causing significant compliance risks; (4) Propose to the board of directors the replacement of the company's compliance management responsible person.
The compliance management responsibilities of the management level mainly include: (1) establishing and improving the compliance management organizational structure according to the decisions of the board of directors; (2) Approve specific regulations for compliance management; (3) Approve the compliance management plan and take measures to ensure the effective implementation of the compliance system; (4) Clarify the compliance management process and ensure that compliance requirements are integrated into the business domain; (5) Timely stop and correct non compliant business behaviors, and investigate the responsibilities of the violators or propose handling suggestions according to their authority; (6) Other matters authorized by the board of directors.
2. The organizational structure of compliance management is: a central enterprise establishes a compliance committee, which cooperates with the corporate legal construction leading group or risk control committee to undertake the organizational leadership and overall coordination of compliance management; The relevant person in charge or general legal adviser of a central enterprise serves as the person in charge of compliance management, and one of their main responsibilities is to report major issues of compliance management to the board of directors and the general manager; Legal affairs agencies or other relevant institutions are the lead department for compliance management, organizing, coordinating, and supervising compliance management work, and providing compliance support to other departments; The business department is responsible for the daily compliance management work in its field, improving its business management systems and processes in accordance with compliance requirements, proactively conducting compliance risk identification and troubleshooting, issuing compliance alerts, organizing compliance reviews, promptly notifying the compliance management lead department of risk matters, properly responding to compliance risk events, and conducting compliance training and business partner compliance investigations in its field, Organize or cooperate in investigating violations and promptly rectify them. Relevant departments such as supervision, audit, law, internal control, risk management, safety production, quality and environmental protection shall perform their compliance management responsibilities within their authority.
4、 What does compliance management do?
Central enterprises should focus on key areas, key links, and key personnel to effectively prevent compliance risks based on comprehensive promotion of compliance management in accordance with changes in the external environment and their own realities. The guidelines list seven key areas, three key links, and three categories of key personnel, and emphasize the compliance operation of overseas businesses.
The seven key areas refer to market transactions, safety and environmental protection, product quality, labor and employment, finance and taxation, intellectual property, and business partners. The three key links refer to the system formulation process, the business decision-making process, and the production and operation process. The three major categories of key personnel refer to management personnel, personnel in important risk positions, and overseas personnel. Among them, personnel in important risk positions refer to functional positions that bear important compliance risks determined through compliance risk assessment. It is required to strengthen the compliance management of overseas investment and operation behaviors.
In the field of market transactions, it is necessary to improve the transaction management system, strictly implement the decision-making and approval procedures, establish a sound self-discipline and integrity system, highlight the fight against commercial bribery, antitrust, and unfair competition, and standardize asset trading, bidding, and other activities;
In the field of safety and environmental protection, it is necessary to strictly implement national laws and regulations on safe production and environmental protection, improve enterprise production specifications and safety and environmental protection systems, strengthen supervision and inspection, and promptly identify and rectify violations;
In the field of product quality, it is necessary to improve the quality system, strengthen process control, strictly control the quality of all links, and provide high-quality products and services;
In the field of labor employment, it is necessary to strictly abide by labor laws and regulations, improve the labor contract management system, standardize the signing, performance, modification, and termination of labor contracts, and effectively safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of workers;
In the field of finance and taxation, it is necessary to improve the internal financial control system, strictly implement the operation and approval process of financial matters, strictly abide by financial discipline, strengthen the awareness of paying taxes according to law, and strictly abide by tax laws and policies; In the field of intellectual property, it is necessary to apply for the registration of intellectual property achievements in a timely manner, standardize the implementation of licensing and transfer, strengthen the protection of trade secrets and trademarks, standardize the use of intellectual property rights of others in accordance with the law, and prevent infringement;
In the field of business partners, it is necessary to conduct compliance investigations on important business partners, and promote business partner behavior compliance by signing compliance agreements and requiring compliance commitments.
5、 How to manage compliance?
The fourth chapter of the guidelines is specific provisions on the operation of compliance management, indicating how to manage compliance for enterprises from six aspects: compliance management system construction, risk early warning, risk response, review mechanism, accountability for violations, and compliance management evaluation.
1. Establish and improve the compliance management system, develop compliance behavior norms that are generally observed by all employees, develop special compliance management systems for key areas, and timely translate external compliance requirements into internal rules and regulations based on changes in laws and regulations and regulatory dynamics.
2. Establish a compliance risk identification and early warning mechanism, comprehensively and systematically sort out the compliance risks existing in business management activities, systematically analyze the possibility, impact degree, potential consequences, etc. of the risks, and timely issue early warnings for risks that are typical, universal, and may have relatively serious consequences.
3. Strengthen compliance risk response, develop plans for identified risks, take effective measures, and respond promptly. For major compliance risk events, the Compliance Committee will provide overall leadership, the compliance management leader will take the lead, and relevant departments will cooperate to minimize risks and losses.
4. Establish and improve a compliance review mechanism, making compliance review a necessary procedure for business management activities such as rule and regulation formulation, major matter decision-making, important contract signing, and major project operation. Timely propose amendments to non compliant content, and do not implement them without compliance review.
5. Strengthen accountability for violations, improve the punishment mechanism for violations, clarify the scope of responsibility for violations, and refine punishment standards. Clear reporting channels, promptly investigate the reported issues and clues, and seriously investigate the responsibility of violators.
6. Conduct compliance management assessments, regularly analyze the effectiveness of the compliance management system, thoroughly identify the root causes of significant or recurring compliance risks and violations, improve relevant systems, plug management gaps, strengthen process control, and continuously improve.
6、 How to ensure compliance management?
Chapter V of the Guidelines stipulates that the effective operation of compliance management is ensured through the following six aspects:
1. Strengthen compliance assessment and evaluation, incorporate compliance operation and management into the annual comprehensive assessment of heads of departments and affiliated enterprises, and refine evaluation indicators. Evaluate the performance of compliance responsibilities of affiliated units and employees, and use the results as an important basis for employee evaluation, cadre appointment, and selection of the best candidates.
2. Strengthen the informatization construction of compliance management, optimize the management process through informatization means, record and save relevant information. Use tools such as big data to strengthen real-time online monitoring and risk analysis of legal compliance of business management behaviors, and achieve information integration and sharing.
3. Establish a professional and high-quality compliance management team, allocate compliance management personnel based on factors such as business scale and compliance risk level, continuously strengthen business training, and improve the team's ability level. For overseas operations in important regions and key projects, it is necessary to clarify the compliance management organization or allocate full-time personnel to effectively prevent compliance risks.
4. Establish compliance training, combine legal publicity and education, establish institutionalized and normalized training mechanisms, and ensure that employees understand and comply with corporate compliance goals and requirements.
5. Actively cultivate a compliance culture, strengthen the awareness of safety, quality, integrity, and integrity of all employees by formulating and issuing compliance manuals, signing compliance commitment letters, and other methods, establish the values of legal compliance, law-abiding integrity, and build a solid ideological foundation for compliance management.
6. Establish a compliance reporting system. In the event of a major compliance risk event, the compliance management lead department and relevant departments should promptly report to the compliance management responsible person and the leader in charge. Major compliance risk events should be reported to the SASAC and relevant departments. The leading department of compliance management comprehensively summarizes the work of compliance management at the end of each year, drafts an annual report, which is reviewed and approved by the board of directors and promptly submitted to the SASAC.
7、 The link between compliance and internal control and risk management
Compliance itself is one of the objectives of internal control and risk management, so internal control and risk management are also means and tools to achieve compliance objectives. The objectives of internal control and risk management are not limited to compliance, and compliance objectives are the basic objectives of all these functions. The promotion of compliance management by enterprises is a systematic and fully engaged professional management activity that is related to all existing management systems of enterprises, but with different focus points and focus points, which often leads to confusion between compliance and internal control, risk management, and legal risk prevention.
In terms of specific work, corporate compliance management is the consolidation and enhancement of the compliance management part and related content in the existing management system of an enterprise, or the separate summary of its related content to the compliance management responsible department to further sort out and improve the formation of a compliance management system. Strengthening compliance management and managing the enterprise according to law, internal control, and comprehensive risk prevention and control are mutually reinforcing and interactive processes, rather than building compliance management from scratch.
Related recommendations
- Tax lawyers review the draft of the revised Tax Collection and Administration Law for soliciting opinions
- New Measures for Punishing "Dishonesty" by the Supreme People's Court at the Two Sessions in 2025 (Part 3): "Height Limit" Single Release Mechanism
- New Measures for Punishing "Dishonesty" by the Supreme People's Court at the Two Sessions in 2025 (Part 2): Grace Period System
- Interpretation of the Management Measures for Compliance Audit of Personal Information Protection - Feeling the Rhythm and Rhythm of Regulatory Flow




