Discussion on several issues of equity incentives of state-owned non-listed companies
introduction
20In the early 90s of the century, in order to solve the outstanding problems such as insufficient development momentum in state-owned enterprises and state-owned enterprise employees eating "big pot rice", the state began to promote and deepen the reform of state-owned enterprises, and one of the important measures was to take the lead in introducing the equity incentive system in state-owned enterprises. In 2006, with the promulgation of relevant laws and regulations, the equity incentives of state-controlled listed companies have been followed by laws and have entered the track of rapid development. However, equity incentives have not played their expected role in state-owned non-listed companies, and even due to the imperfect relevant laws and policies, coupled with strict state-owned asset supervision and cumbersome approval procedures, equity incentives have become a system design that state-owned non-listed companies dare not touch. So, under the current conditions, is the equity incentive of state-owned non-listed companies suitable for implementation and how can it be implemented? This article will attempt to explore the above questions.
1. Legal and policy support for state-owned enterprises to implement equity incentives
Since the 90s of the 20th century, equity incentives, as a supporting measure for the deepening of the reform of state-owned enterprises, have roughly experienced the following development stages:
(i) From the 90s of the 20th century to 2004 - the initial and exploratory stage
1998Since the beginning of the year, some places in China have begun to explore the trial implementation of the stock option system by state-owned enterprises. The Decision of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on Several Major Issues Concerning the Reform and Development of State-Owned Enterprises, issued in 1999, provides policy support for equity incentives in state-owned enterprises, that is, "establishing and improving incentive and restraint mechanisms for the operation and management of state-owned enterprises." Implement the linkage between the income of business managers and the business performance of enterprises. .... A small number of enterprises have experimented with the annual salary system of managers (factory directors) and the distribution methods of holding equity. In the same year, Wuhan, Shanghai and Beijing successively formulated relevant policies, with a total of about 30 pilot enterprises. In 2002, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Science and Technology jointly issued the Guiding Opinions on the Pilot Work of Equity Incentives in State-owned High-tech Enterprises, which proposed for the first time to carry out equity incentive pilots in state-owned high-tech enterprises. In 2004, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC) promulgated the Interim Measures for the Management of the Remuneration of Heads of Central Enterprises, proposing to gradually promote medium- and long-term incentive measures such as stock options on the basis of standardized management.
(ii) From 2005 to 2008 - initial development and progress towards the legalization stage
2005The amendment to the Company Law added a circumstance under which a company may acquire shares of the Company, that is, "awarding shares to the employees of the Company". In 2006, the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) promulgated the Administrative Measures for Equity Incentives of Listed Companies (for Trial Implementation). In the same year, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC) and the Ministry of Finance jointly issued the Trial Measures for the Implementation of Equity Incentives for State-Controlled Listed Companies (Overseas) and the Trial Measures for the Implementation of Equity Incentives for State-Controlled Listed Companies (Domestic) also came into effect. Since then, the equity incentives of China's state-owned enterprises, especially state-controlled listed companies, have entered the track of legalization. Affected by the three trial measures promulgated in 2006, the number of equity incentives implemented in state-owned enterprises peaked in 2008.
(c) From 2008 to 2010 - a period of clean-up, regulation and slow development
In the process of promoting the shareholding reform of state-owned enterprises, due to the imperfect laws and regulations related to equity incentives and the lack of operable guidance, some problems have occurred in state-owned enterprises in the process of employee shareholding. In 2008 and 2009, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC) issued documents regulating employee shareholding and investment. The Ministry of Finance also cleaned up and halted equity incentives and employee stock ownership plans for state-owned and state-controlled financial enterprises during the same period. It was not until 2010 that equity incentives for state-owned enterprises continued to be promoted.
2010In February of that year, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Science and Technology jointly issued the "Implementation Measures for Printing and Distributing the Implementation Measures for Enterprise Equity , Dividend Incentives in the Zhongguancun National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone < Zhongguancun > The Measures are applicable to state-owned and state-controlled institutions in the Zhongguancun National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone, high-tech enterprises, enterprises in which institutions of higher learning and scientific research institutes in the demonstration zone have invested shares in scientific and technological achievements, and other scientific and technological innovation enterprises. Since then, the field of high-tech enterprises has become the main position for carrying out equity incentive pilots. ober 2010, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC) issued the Notice on Carrying out the Pilot Work of Incentive for Dividend Rights in Some Central Enterprises. Since then, state-owned enterprises have begun to select exemplary enterprises in subdivided industries, provide guidance on distinguishing situations and classifications, and actively and prudently restore and continue to promote the implementation of equity incentives for state-owned enterprises by formulating specific operational specifications.
(4) The Third Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee in 2013 has been held since the beginning of rapid development
2013The Third Plenary Session of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China adopted the Decision of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on Several Major Issues Concerning the Comprehensive Deepening of Reform, which proposed that "mixed ownership economies are allowed to implement employee shareholding in enterprises and form a community of interests of capital owners and laborers." ince then, employee shareholding in state-owned enterprises has had strong policy support. arch 1, 2016, the Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Science and Technology and the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission jointly issued the Interim Measures for Equity and Dividend Incentives for State-Owned Science and Technology Enterprises (Caizi [2016] No. 4, referred to as "Document No. 4 of 2016") came into effect. The Measures provide detailed and clear provisions on how state-owned science and technology enterprises implement equity incentives. In August 2016, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission, the Ministry of Finance and the China Securities Regulatory Commission jointly issued the Opinions on the Pilot Project of Employee Shareholding in State-Controlled Mixed Ownership Enterprises (State-owned Assets Development Reform (2016) No. 133, referred to as "Document No. 133 of 2016"). ), put forward practical guidance for state-controlled mixed ownership enterprises to carry out employee shareholding pilots. Subsequently, various local provinces and cities successively issued supporting implementation rules for state-controlled mixed-ownership enterprises to carry out employee shareholding pilots. Shanghai, Guangdong, Fujian and other provinces and cities are at the forefront of carrying out employee stock ownership pilots, and have formulated implementation rules for employee stock ownership pilots. <In 2017, Shanghai released three batches of pilot lists of employee shareholding, and 9 enterprises, including Shanghai Electric Guoxuan New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Qi Cheng Network Technology Co., Ltd., and Shanghai Comprehensive Bonded Zone International Logistics Co., Ltd., were listed; Guangdong also released the first batch of employee shareholding pilot lists in the same year, and three enterprises, including Guangzhou Institute of Building Research Co., Ltd., Guangzhou Zhujiang Amoson Digital Musical Instrument Co., Ltd., and Hualian Futures Co., Ltd., were listed. In addition, Beijing, Liaoning, Sichuan, Shanxi, Anhui, Gansu, Tianjin, etc. have also successively issued relevant policies to support and standardize the deployment of employee shareholding pilot work.
2017In November of that year, eight ministries and commissions, including the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, jointly issued the "Opinions on Several Policies for Deepening the Pilot Mixed Ownership Reform", which pointed out that "adhere to the principles of legal compliance, openness and transparency, based on increment, immovable stock, same share price, cash investment, fixed shares by post, and dynamic adjustment, and actively promote employee shareholding in pilot enterprises of mixed ownership reform." .... The number of pilot enterprises is not subject to the quantitative limit stipulated in Document No. 133. ince then, equity incentives and employee stock ownership plans have broken through the restrictions of state-owned enterprises in the industry field, expanding from state-owned science and technology enterprises to all industries except state-owned financial enterprises. In October 2019, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC) issued the Operational Guidelines for the Reform of Mixed Ownership of Central Enterprises, which once again reiterated that "mixed-ownership enterprises are encouraged to comprehensively use medium- and long-term incentive policies such as employee shareholding in state-controlled mixed-ownership enterprises, equity incentives for state-controlled listed companies, and equity and dividend incentives for state-owned science and technology enterprises".
(5) Summary
In summary, although the equity incentive of state-owned enterprises fluctuates slightly in the process of development, it is on the rise as a whole. Initially, equity incentives for state-owned enterprises were only carried out in science and technology enterprises, but now they have been extended to enterprises in almost all fields except financial state-owned enterprises. The equity incentive model has also been gradually enriched from equity awards, technical stock conversion, dividend rights, etc. to stock options, restricted equity and employee stock ownership plans. Since 2006, equity incentives have moved towards the stage of legalization, and the operability of relevant laws and policies has gradually increased. Especially since 2016, state-owned non-listed companies in various places have become more and more enthusiastic about carrying out equity incentive pilots, and there are more and more successful cases. It can be seen that state-owned non-listed companies are gradually breaking the embarrassing situation of not daring to try equity incentives, and are developing rapidly with a standardized and legal attitude.
2. Example of successful case - China Electrical Appliance Employee Stock Ownership Plan
1China Electrical Equipment Research Institute Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "China Electrical Appliances") was founded in 1958, under the central government's important state-owned backbone enterprise - China Machinery Industry Group Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Sinomach Group"), which integrates scientific research and development, scientific and technological services, A state-level innovative technology enterprise integrating the three core business sectors of the science and technology industry. Sinomach Group, the controlling shareholder of China Electric Appliances, directly holds 54% of the shares of China Electric Appliances, and indirectly holds 6% of the shares through its holding subsidiary, Sinomach Capital, for a total of 60% of the shares.
2016In November, China Electric was approved to become one of the first 10 enterprises in the central enterprise to carry out the employee shareholding pilot. China Electric hopes to effectively solve the problem of serious loss of core talents and bottleneck of enterprise development through the implementation of employee stock ownership plan. The main elements of the China Electrical Appliance Employee Stock Ownership Plan are as follows:
(1) Shareholding mode - capital increase and share increase + employee shareholding
China Electric follows the principle of "incremental introduction, interest binding, fixed shares by post, and dynamic adjustment", and adopts capital increase and share expansion to carry out employee shareholding.
(2) Incentive targets and number of shares
The incentive targets are scientific research personnel, business management and business backbones who work in key positions and have a direct or greater impact on the company's business performance and sustainable development, mainly including employees in middle-level positions and above in the company and core backbone personnel engaged in scientific research, management and market development.
The total shareholding ratio of China Electric Employee Stock Ownership Plan is 27%. In addition, China Electric Corporation reserves 1% of the company's equity for the incentive of new key employees. See the table below for details:
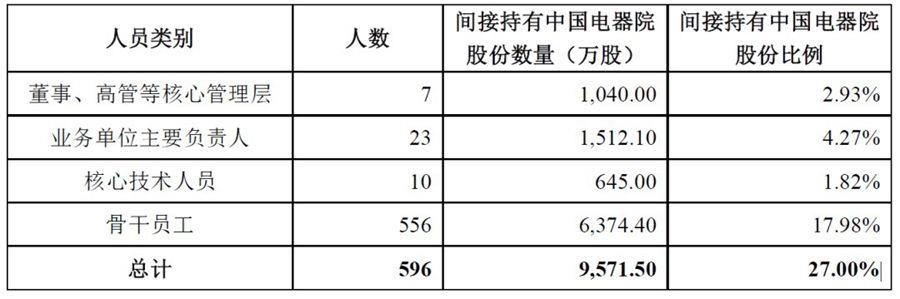
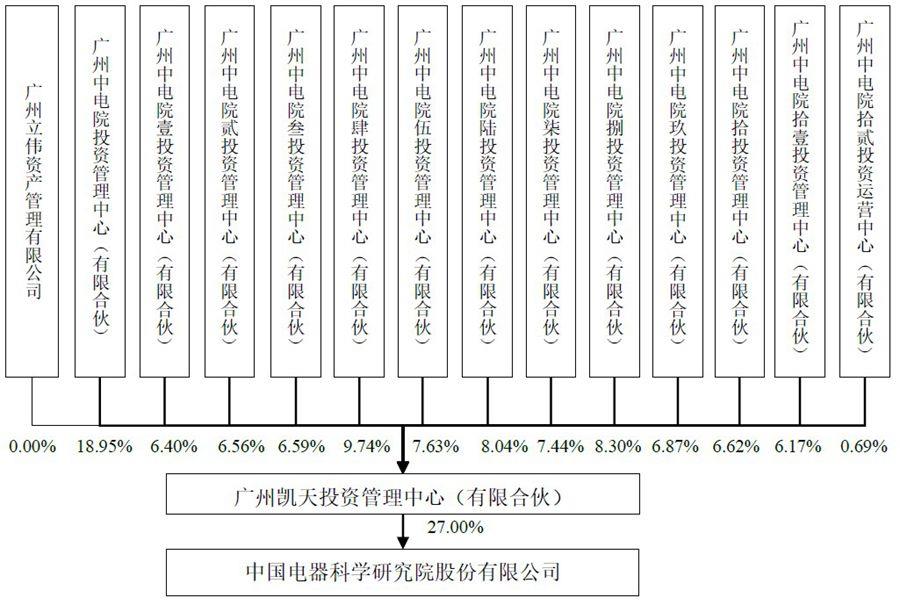
(6) Implementation effects
By adopting the two-pronged measures of "mixing shares and reforming the mechanism", China Electric has entered the fast lane of development. 2017, the amount of new contracts signed by China Electrical Appliances increased by 40% year-on-year, operating income increased by 26% year-on-year, and total profit increased by 50% in the same caliber. In particular, employee stock ownership plans solve the problem of companies not retaining talent. Before employee stock ownership, the annual turnover rate of China Electric employees was about 10%, and after the introduction of the employee stock ownership plan, it dropped to about 4%.
2019On October 25, China Electric (stock code: 688128) successfully listed on the Science and Technology Innovation Board on the Shanghai Stock Exchange. From the approval of the employee stock ownership pilot in November 2016 to the successful listing of the Science and Technology Innovation Board in October 2019, China Electric took less than 3 years, which shows the strong empowerment of China Electric Appliance under the employee stock ownership plan.
In addition to the successful implementation of equity incentives by China Electric Appliances, in 2007, Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co., Ltd. launched the first equity incentive plan before the listing of A-shares on the small and medium-sized board of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange; 2017, Ouyeel Yunshang Co., Ltd. simultaneously launched an employee stock ownership plan when introducing strategic investors such as Beijing Shougang Fund Co., Ltd., and Shandong Communications and Transportation Group Co., Ltd. publicly listed strategic investors through Shandong Property Rights Exchange Center and implemented an employee stock ownership plan at the same time; 2018, Hebei North China Pharmaceutical Huaheng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. implemented the "old shareholders' capital increase and share expansion + employee stock ownership plan" Harbin Power Station Equipment Design Institute Co., Ltd. listed on the Shanghai United Equity Exchange to introduce two strategic investors, Hangzhou Boiler Group Co., Ltd. and Heilongjiang Taizheng Investment Group Co., Ltd., and simultaneously carried out employee stock ownership plans, etc., are all successful cases of state-owned non-listed companies implementing equity incentives and achieving good results, which shows that the practice of equity incentives of state-owned non-listed companies has gradually developed.
3. Basic principles and general operating norms for the implementation of equity incentives by state-owned non-listed companies
Although there is no unified legal provision on equity incentives for state-owned non-listed companies, it is scattered in 2016 such as Circular No. 133 and Circular 4, as well as policy documents of central and local governments. However, by analyzing the above documents and combining some equity incentive cases of state-owned non-listed companies, the author summarizes the following basic principles and general operating norms that state-owned non-listed companies need to follow in implementing equity incentives.
(1) The basic principles for implementing equity incentives for state-owned non-listed companies
1, comply with laws and regulations, be fair and transparent, and prevent the loss of state-owned assets.
Therefore, strictly abiding by the state's laws and regulations on state-owned asset supervision, ensuring that the operation process is fair and transparent, preventing the loss of state-owned assets, and maintaining the preservation and appreciation of state-owned assets are the most basic principles and prerequisites that need to be followed in the process of implementing equity incentives for state-owned non-listed companies. This is mainly manifested in:
First, the equity incentive plan must be approved or filed by the state-owned assets regulatory authority. For example, Document No. 4 of 2016 stipulates that "incentive plans shall be submitted to the departments, institutions and enterprises performing the regulatory duties of investors or state-owned enterprises for approval". Document No. 133 of 2016 stipulates that "the employee stock ownership plan of the local pilot enterprise shall be reported to the institution performing the duties of the investor for the record, and at the same time copied to the state-owned assets supervision and management agency of the provincial people's government; The employee stock ownership plan of the central pilot enterprise shall be reported to the institution performing the duties of the investor for the record".
Second, the purchase price is subject to asset valuation and must not be less than the approved or filed appraised value of net assets per share. The company shall not donate equity to employees free of charge, and shall not provide holders with financial assistance such as capital advances, guarantees, loans, etc.
Third, related party transactions should be regulated in the process of implementing incentives for rights. For example, Document No. 133 of 2016 stipulates that "the shareholding platform as an employee stock ownership plan shall not engage in any business activities other than shareholding". Document No. 4 of 2016 stipulates that "if indirect shareholding is adopted, the shareholding entity shall not have intra-industry competition with the enterprise or engage in related party transactions".
Fourth, after the completion of equity incentives, the controlling position of state-owned shareholders should still be maintained.
2Combination of incentives and constraints, benefit sharing, risk sharing.
Equity incentives are not equity benefits. In the process of implementing equity incentives in state-owned enterprises, it is necessary to avoid the situation of employees eating "new cauldron rice", establish and improve the long-term mechanism of incentives and constraints, and at the same time handle the relationship between the short-term returns of shareholders and the medium- and long-term development of the company, form a bundle of interests through equity incentives, and share the risks of market competition and the fruits of development between the company and employees, in order to achieve a win-win situation.
(2) General operating norms for the implementation of equity incentives by state-owned non-listed companies
Based on the relevant laws and policies of state-owned enterprises on equity incentives and the aforementioned basic principles, combined with relevant cases, and in accordance with the six main elements of equity incentives, namely, fixed objects, fixed models, fixed quantities, fixed prices, fixed sources and fixed conditions, the author attempts to summarize the general operating norms for the implementation of equity incentives by state-owned non-listed companies as follows:
1, targeted
The incentive targets of equity incentives for state-owned non-listed companies are mainly for important technical and operational management personnel, key positions and core backbone personnel who have signed labor contracts with the company, and in principle, they are not allowed to hold all shares, and do not engage in new "egalitarianism". At the same time, due to the particularity of the status of state-owned enterprises, there is also a negative list of incentive targets, for example, according to Document No. 133 of 2016, "leaders of state-owned enterprises appointed by the Party Central Committee, the State Council, local party committees, governments, and their departments and institutions shall not hold shares." Outside directors and supervisors (including employee representative supervisors) do not participate in employee shareholding. If there are multiple immediate family members in the same enterprise, only one person can hold the shares".
2, set the mode
The incentive models that state-owned non-listed companies can adopt mainly include equity sales, equity awards, equity options, dividend rights incentives and employee stock ownership plans. Enterprises can choose the appropriate incentive model based on factors such as their own enterprise scale, industry characteristics, development stage, and legal policy support
3, a fixed quantity
In order to ensure that the state-owned controlling status is not changed due to the implementation of equity incentives, the implementation of equity incentives by state-owned non-listed companies has certain restrictions on the number and proportion of shares held by employees. For example, Document No. 133 of 2016 stipulates that "in principle, the total shareholding ratio of employees shall not be higher than 30% of the total share capital of the company, and the shareholding ratio of a single employee shall not be higher than 1% of the total share capital of the company in principle". Document No. 4 of 2016 stipulates that "the total amount of equity incentives of large enterprises shall not exceed 5% of the total share capital of the enterprise; The total equity incentive of a medium-sized enterprise shall not exceed 10% of the total share capital of the enterprise; The total amount of equity incentives of small and micro enterprises shall not exceed 30% of the total share capital of the enterprise, and the incentive equity obtained by a single incentive target shall not exceed 3% of the total share capital of the enterprise. A single incentive recipient who receives an equity award must purchase the equity of the enterprise at a ratio of not less than 1:1, and the equity award obtained shall be converted according to the appraised value at the time of implementation of the incentive, and the cumulative amount shall not exceed 3 million yuan".
4, set the price
In order to prevent the loss of state-owned assets, employees need real money to contribute capital when state-owned non-listed companies implement equity incentives. The employee purchase price is subject to asset valuation and must not be lower than the approved or filed appraised value of net assets per share.
In addition, the existing laws and regulations on equity incentives issued by the central government do not clearly stipulate whether employees must be listed on the equity exchange. In practice, it is common practice that state-owned non-listed companies implement equity incentives simultaneously when initiating mixed reform and introducing investors, and investors need to enter the market to determine the equity price through auction, and the incentive target will contribute capital to purchase equity according to the equity price listed by the investor. It should be pointed out that the "Implementation Plan for the First Batch of Pilot Work on Employee Shareholding in Local State-Controlled Mixed Ownership Enterprises in the City" jointly issued by the Shanghai State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission, the Finance Bureau, the Financial Affairs Office, and the China Securities Regulatory Bureau clearly stipulates that "non-listed companies may not enter the market to implement employee shareholding by way of capital increase and share expansion, and the investment price shall not be lower than the assessed value". Therefore, with the development and maturity of the practice of equity incentive of state-owned non-listed companies, the national level may also have a positive attitude towards the fact that employees of state-owned non-listed companies do not need to enter the bidding transaction to obtain incentive equity.
5, Definitive source
The state encourages the use of equity increments formed by capital increases or new companies to implement equity incentives, but does not exclude the use of methods of repurchase from existing shareholders or transfer of equity by existing shareholders to incentive recipients in accordance with the law to solve the problem of the source of incentive shares.
6, set conditions
The conditions include both the access conditions of state-owned non-listed companies implementing equity incentives, and the performance appraisal conditions that need to be completed during the implementation process and the incentive recipients.
Not all state-owned non-listed companies can or are suitable for implementing equity incentives, and the state has set different access conditions for the implementation of equity incentives for state-owned non-listed companies in different situations. In principle, the state encourages and supports commercial state-owned enterprises with a high proportion of human capital and technical elements, clear property rights, standardized management, and the main business in industries and fields where the main business is fully competitive to carry out equity incentives.
In addition, in the process of implementing equity incentives, state-owned non-listed companies should agree on performance assessment targets with incentive recipients, or link the positions of incentive targets with performance, so as to achieve the strategic goals of attracting and retaining talents, achieving economic growth and preserving and increasing the value of state-owned assets.
(3) Summary
However, because each state-owned enterprise is located in the industry, characteristics and scale, development stage, state-owned legal support for equity incentives, policy orientation, equity incentive practice development maturity, etc. or is different, therefore, state-owned non-listed companies in the specific practice of implementing equity incentives. In addition to grasping the above basic principles and general norms, you should also pay attention to the specific analysis of specific projects according to your own situation, and communicate with relevant approval and regulatory authorities in advance to ensure that the implementation process of equity incentives is in compliance with the law.
IV. Conclusion
To sum up, from the historical evolution of the laws and policies on the reform and implementation of equity incentives in state-owned enterprises, it can be seen that the central and local governments have issued relatively complete legal regulations and good policy orientation, and state-owned non-listed companies have the external conditions and environment for implementing equity incentives. Recently, some state-owned non-listed companies have carried out equity incentive and employee stock ownership pilot programs in full swing. The author believes that state-owned non-listed companies with conditions should seize this new opportunity and a good social environment atmosphere, grasp the basic principles and general norms of the implementation of equity incentives by state-owned non-listed companies under the premise of complying with relevant national laws and regulations and following the guidance of national policies, summarize and absorb the relevant successful experiences of other enterprises, prudently promote the implementation of equity incentive plans according to the conditions of enterprises, and strive to achieve leapfrog growth in economic benefits of enterprises through the development and empowerment of equity incentives, and make state-owned non-listed companies bigger and stronger. Even achieve the strategic goal of going public.
(This article is translated by software translator for reference only.)
Related recommendations
- Tax lawyers review the draft of the revised Tax Collection and Administration Law for soliciting opinions
- New Measures for Punishing "Dishonesty" by the Supreme People's Court at the Two Sessions in 2025 (Part 3): "Height Limit" Single Release Mechanism
- New Measures for Punishing "Dishonesty" by the Supreme People's Court at the Two Sessions in 2025 (Part 2): Grace Period System
- Interpretation of the Management Measures for Compliance Audit of Personal Information Protection - Feeling the Rhythm and Rhythm of Regulatory Flow


